This article contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase after clicking on a link I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Barrier function is an important concept in understanding and treating allergy/sensitivity. Barrier functions are those things that keep the patient from becoming sensitized (experiencing a negative body response) to substances.
There are three major barriers and some supporting organs to consider.
[box size=”large” style=”rounded”]The barrier function for food sensitivity or intolerance is digestion. If the patient can digest and metabolize normally, they do not become sensitized to foods.[/box] 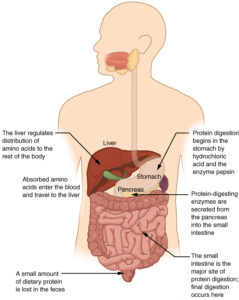
Inadequate digestion for any reason (infection, inflammation, malabsorption) may result in digestive barrier default, and particles that are too large are absorbed into the bloodstream. If that occurs, sensitization becomes a random event. That is, the patient may or may not become sensitized to any food or chemical constituent or metabolite of that food.
Substances highest in the patient’s food chain (the things they eat the most) are the most suspect. Remember that due to digestion and delayed (rather than immediate) hypersensitivity responses, it is very difficult to correlate food symptoms to exposure.
Allergy testing must consider IgG as well as IgE antibodies to foods.
The second, most difficult, barrier to assess and control is for inhaled substances (dust, pollens, dander, molds, etc.) That barrier is the mucus that covers the membranes of the sinuses and respiratory passages. If there is too much mucus, the passages can’t drain and infection results. The purpose of the mucus is to trap any irritants and particulates so that they do not come in contact with the membranes and can be removed (blowing the nose, sneezing, or coughing).
If the nose, sinuses, or respiratory passages have areas without mucus, however, a pollen that comes in direct contact with the membrane may irritate it enough so that the pollen is absorbed into the bloodstream and sensitization occurs. Adequate fluid intake, humidification of the air, nasal application of isotonic saline drops, and use of mucilaginous plant substances (slippery elm, plantain, marshmallow root) are protective measures for the mucous membranes.
The third barrier is the skin.
Any break in the skin (cut, scrape, burn, rash, or other skin defect) compromises the barrier. Sensitization may occur with any substance that comes in contact with that area of the skin. Cosmetics, eyeglasses, jewellery, perfumes, deodorants, sunscreen, as well as skin organisms are all commonly sensitized.
Organs that support the barrier functions are the adrenal, thyroid, and endocrine glands, and the pancreas, which regulates blood sugar.
Numerous factors can lead to functional defaults in all three barriers and their support organs.
